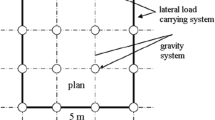
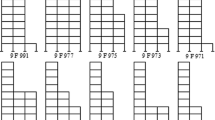
Abstract
Irregular buildings constitute a large portion of the modern urban structures. Based on experiences of past earthquakes, irregular configuration of buildings or asymmetrical distribution of structural properties trigger an increase in seismic demand, intensifying the vulnerability of the structure. In this work, the effects of splitting in levels, classified as vertical irregularity, on the seismic behaviour of some 3D steel structures are studied. Studied models consisted of five-, ten- and fifteen-storey 3D steel special moment-resisting frames, split just in one direction, with six different plans. Equivalent static method together with a special pattern for distributing the base shear, named Level-Based Distribution Method, and also response spectrum analysis, both based on ASCE 7–16 and UBC 97, were used for studying all the models. It was observed that for lateral force distribution, UBC 97 method led to better correlation between static and dynamic results compared to ASCE 7–16 for this category of structures. Moreover, the obtained results revealed that splitting gives rise to developing less total base shear in the lower level columns compared to that in the higher ones. Furthermore, the effects of ‘accidental torsion’ on split-level structures are approximately the same as those on their regular counterparts in the direction of splitting but much less in the perpendicular direction.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
AISC. (2017). Steel construction manual (15th ed.). American Institute of Steel Construction.
Al-Ali, A. A. K., & Krawinkler, H. (1998). Effects of vertical irregularities on seismic behavior of building structures. Report No. 130, John A. Blume Earthquake Engineering Center, Dept. of Civil and Environmental Eng., Stanford University, Stanford, CA.
ANSI, AISC 360–16. (2019). Specification for structural steel buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction.
Arnold, C. (2001). Architectural considerations. In F. Naeim (Ed.), The seismic design handbook (2nd ed., pp. 275–326). Van Nostrand Reinhold.
ASCE, SEI. (2016). Minimum design loads for buildings and other structures: ASCE standard 7–16. American Society of Civil Engineers.
Das, S. (2000). Seismic Design of Vertically Irregular Reinforced Concrete Structures. PhD thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC.
Das, S., & Nau, M. (2003). Seismic design aspects of vertically irregular reinforced concrete buildings. Journal of Earthquake Spectra, 19(3), 455–477.
Horne, M. R., & Merchant, W. (1965). The stability of frames. Pergamon Press.
Humar, J. L., & Wright, W. (1977). Earthquake response of steel framed multistory buildings with set-backs. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 5(1), 15–39.
Kheyroddin, A., & Mirnezami, A. (2004). Investigation of nonlinear behavior of connections in split-level buildings frames. Proceedings of the 1st National congress of civil engineering, Tehran, Iran, May 11–13, paper 83–1674. (in Persian).
Khonsari, S. V., England, G. L., & Kiani, M. (2010). Investigating the seismic behaviour of split-level building structures. In: Proceedings of the 9th U.S. National and 10th Canadian conference on earthquake engineering, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, July 25–29, paper 1445.
Kiani, M. (2008). Seismic Behavior of Split-Level Steel Moment Resisting Frames. MSc Thesis, Department of Civil Eng., Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran (in Persian).
Monish, S., & Karuna, S. (2015). Effect of Vertical Irregularity in RC Framed Buildings in Severe Seismic Zone. International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering, 5(6).
Tremblay, R., & Poncet, L. (2005). Seismic performance of concentrically braced steel frames in multistory buildings with mass irregularity. Journal of Engineering Structures., 131(9), 1363–1375.
UBC (Uniform Building Code, 1997). International conference of building officials, Whittier, CA.
Valmundsson, E. V., & Nau, J. M. (1997). Seismic response of building frames with vertical structural irregularities. Journal of Structural Engineering, 123(1), 30–41.
Varadharajan, S. (2014). Study of Irregular RC Buildings under Seismic effect. PhD Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology Kurukshetra, Kurukshetra, India.
Wilson, E. L. (2002). Three-dimensional static and dynamic analysis of structures, a physical approach with emphasis on earthquake engineering (3rd ed.). Computers and Structures Inc.
Wong, M. B. (2009). Plastic analysis and design of steel structures. Elsevier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khonsari, S.V., Eskandaritorbaghan, F. Investigation into the 3D Behaviour of Split-Level Steel Building Structures: Introducing the LBDM. Int J Steel Struct 22, 833–850 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-022-00607-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-022-00607-0